Voltage converters - from 12V DC to 230V AC using inverters
Voltage converters are a clever solution for using electricity wherever a battery is available. The most common variant converts 12V direct current into 230V alternating current, which is required by common household appliances. Of course, other conversion ranges are also possible.
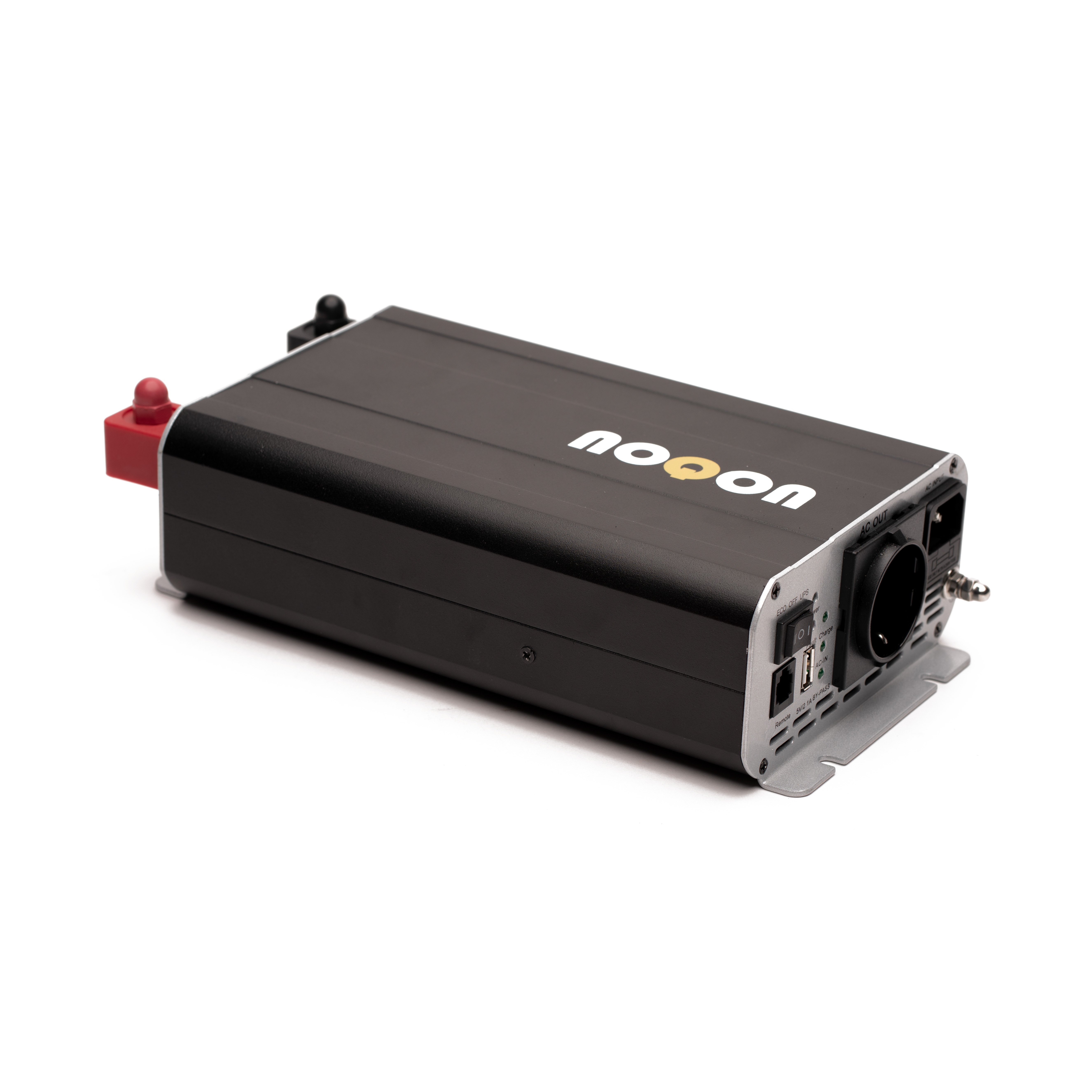
Voltage converters - also called inverters or inverters - are available in a variety of designs. From the practical small format with USB connection for charging cell phone batteries in the car to high-performance machines that lack no sophistication.
What is an inverter?
Electrical appliances require either direct or alternating current to operate. Devices that are operated with alternating current have usually been developed for use via the socket and are therefore more common worldwide than devices that are operated with direct current. Especially in the context of mobile life, there is not always a socket available to supply devices with the required alternating current. It is precisely in such situations that inverters are used. An inverter is an electrical device that is able to convert direct current into alternating current and thus supply the appliances with the correct and required power. The inverter uses the existing direct current source, such as a starter or supply battery of a truck, boat, camper, etc., and converts it into an alternating voltage. This makes it possible to use a wide variety of 230V electrical appliances anywhere and at any time, even though only a DC voltage source is available.
Why do I need an inverter?
Voltage converters create great things and are versatile gadgets that can make trips even more enjoyable. In addition to their use in the home with photovoltaic systems, they are a good way to obtain flexible power on the move - for example in the car. Here, voltage converters offer the opportunity to continue working on the move when the laptop battery is running low. The power of around 100 watts required by the laptop's mains adapter can also be supplied by the cigarette lighter. Even at festivals, the smartphone battery is quickly fully recharged thanks to the inverter.
However, the inverter is also particularly practical in motorhomes. Here, it ensures that even large appliances can be operated without any problems. Televisions, coffee machines, fridges or even music systems for a great party in the open air can be used in this way. Of course, a sufficient energy reserve is essential for their operation. In this case, it is also advisable to use a sine wave inverter. The sine wave voltage converter maintains a constant voltage. Voltage fluctuations can lead to damage, especially with sensitive appliances.
The choice of inverters is also enormous. These devices can provide up to 4,000 watts of continuous power. With larger appliances in particular, it is advisable to pay attention to integrated protective devices. Overheating protection, overload and short-circuit protection can be worth their weight in gold. A battery monitor also has advantages. Sockets with earthing contact should also be part of the inverter's equipment. Specialist retailers can provide the advice you need to keep track of the wide range of products on offer.
What is the difference between a modified sine wave and a pure sine wave?
Inverters can be divided into two forms of alternating current output. On the one hand, there are inverters with a modified sine wave and, on the other, inverters with a pure sine wave. It is important to understand here that the normal household current is output in a perfect sinusoidal alternating voltage. Inverters with a modified sine wave usually do not manage to imitate the alternating voltage of the household current perfectly. The result is a more staircase-shaped sine wave due to much cheaper production and lower acquisition costs. Such inverters with a modified sine wave are generally quite suitable for the use of simple consumers, provided that no electronic circuits or electrical components are installed. With more sensitive devices, however, the use of such inverters can lead to negative surprises. Devices such as computers, consumer electronics, more complex kitchen appliances, coffee pod machines or modern refrigerators can become very hot, malfunction or not work at all.
In order to avoid such situations, inverters with a pure sine wave should be used. These use a more complex technology to subsequently smooth the AC voltage output and are therefore able to perfectly imitate the voltage of the household current required for such appliances. The installation of such expensive electronics and circuits, as well as significantly higher wattages, usually makes inverters with a pure sine wave considerably heavier and more expensive. Nevertheless, you should think ahead! To avoid having to buy a second inverter in the future, it often makes more sense to opt for the high-quality alternative - inverters with a pure sine wave - right from the start. They allow significantly greater flexibility and compatibility in their use immediately after purchase compared to inverters with a modified sine wave.
Correct key figures make the selection easier
In order to select the right inverter, you must of course know the area of application of the device. For example, is it going to be a trip through the USA where European devices can still be used? The necessary voltage converters are also available for this. In contrast to the European standard of 230 V and 50 Hz, the US uses its own regulations and relies on 110 V at 60 Hz. This apparently small change can seriously damage our appliances.
Otherwise, selecting a suitable inverter is more a matter of adding up the individual properties that the inverter must have. Basically, you need to know what AC voltage is available - 12V, 24V and other sizes are available. If you stick to cars or motorhomes, you usually get 12V.
The next variable is the consumption of the appliances to be operated. They add up to the continuous power. It is important here that all appliances are included in the result of the wattage figures. No light bulb, no matter how small and apparently insignificant, should be forgotten. On the other hand, it should be noted that the voltage converter has an efficiency of 80 to 95 percent. This fact should be reflected in the calculations for the purchase decision. It is also advisable to increase the continuous power value by a further 50 percent based on the loads being operated. The starting power alone of some appliances - such as televisions or microwaves - is many times higher than their specified rated power or service.
Of course, it is also important to consider where the electricity is to come from before using an inverter. The cigarette lighter in a car is designed for a maximum output of 150 watts. This power source would therefore not be sufficient to operate a coffee machine at a festival or on your trip. It already requires 600 to 1,300 watts.
It isbetter to have too much than too little. In the best case scenario, this sum should be less than the specified wattage of the available inverter to cover all eventualities. Regardless of the type of inverter used, it should also be noted that the loads are switched on one after the other and never via multiple sockets. Secondly, it is important to switch on appliances with the greatest demand first.
Things you should not do with a voltage converter
Voltage converters can be the perfect piece of equipment in many areas. However, there are a few points you should always bear in mind when using an inverter. Like many devices that operate at peak performance, voltage converters also get hot over time. Although the fans and ventilators in the device do their best to prevent overheating, they can only do this if there is sufficient air. The inverter therefore needs space. Of course, the cooling systems of the device will also cause noise. This source of noise should definitely be taken into account.
At the same time, it is advisable not to make too much use of the voltage converter in the car. If the car battery is regularly discharged by more than 40 percent, this can damage the battery. If you use a voltage converter from 12V to 230V in a motorhome with a second battery, this provision naturally only applies to a limited extent. To prevent damage to the battery or even complete discharge, it is advisable to purchase and use an inverter with overload protection.
So-called battery monitors ensure that the car can still be started even after the voltage converter has been used. Inverters not only ensure that appliances can run thanks to available electrical energy. They also need a lot of it. They are real power guzzlers. Inverters should therefore only be switched on when they are really needed. Stand-by mode, as with other electrical appliances, is therefore not recommended.